Objective tests measure one’s ability to remember facts & figures understanding of course materials. These tests are often designed to make test-takers think independently. Good objective tests require test-takers to employ high level critical reasoning and make fine discriminations to determine the best answer
Objective Tests. ‘
The most common objective test questions are:
- multiple-choice
- true-false
- matching items
- cloze
The most common is the multiple choice question (MCQ) test where students must select the correct answer from a number of possible answers.
The incorrect answers in MCQs are termed distractors.
Distractors should cotnain:
- misconceptions
- partly correct answers
- common errors of fact or reasoning (these distract students who are not well prepared for the test from giving the correct answer)
MCQs are usually used to test the test-taker’s ability to:
- recall information
- interpret data/diagrams
- analyse/evaluate material
Main strengths of MCQs:
- test a wide range of issues in a short time
- assessment is not affected by a student’s ability to write
- can be reliably marked as all answers are predetermined
- can be quickly marked by computer
- computer marking gives easy access to an item analysis of questions to pinpoint problem areas for students
- a large bank of questions can be built up to reduce future preparation time
- can be used for quick revision at the start or end of a class and marked by the students
Main weaknesses of MCQs:
- do not test the student’s ability to develop and organize ideas and present these in a coherent argument
- takes a long time to write plausible distractors (especially in cases where higher order cognitive skills are being tested)
- restrictions are placed on the test-taker’s answers as they must select from given alternatives
- guessing may result (but plausible distractors will result in intelligent guessing)
- questions are often re-used which means special attention to security
- questions need to be pre-tested and items reviewed to ensure the validity of the items
Writing MCQs is a relatively difficult task. However, the effort expended in item construction is rewarded by the ease and reliability of marking
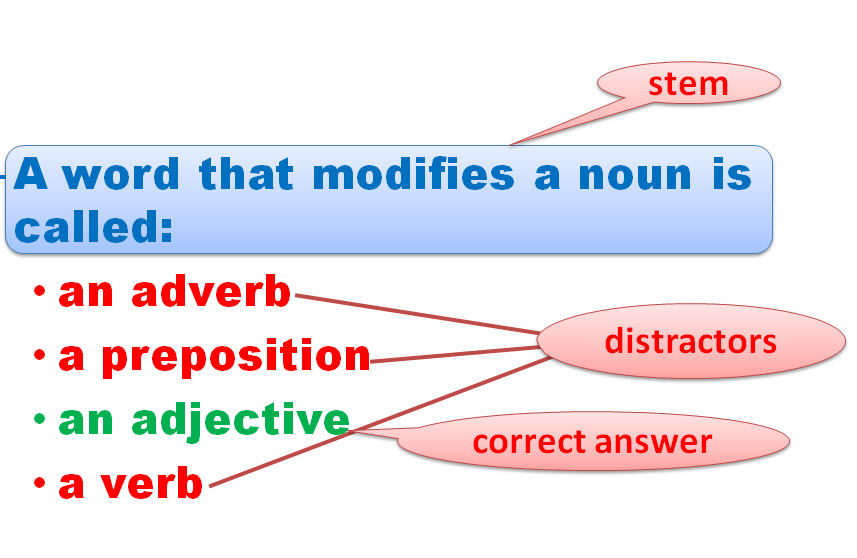
MCQs must have:
a clear and unambiguous stem
a correct answer
several (usually 3 or 4) distractors which appear plausible to students who do not know the correct answer
coherence to the content matter to be examined
E.g.
Tips for constructing MCQs:
- use simply worded stems
- present only one issue in the stem
- avoid use of negative premises (may especially disadvantage ESL students)
- ensure that the answer to one question cannot be obtained from another
- Keep the distractors brief and as homogeneous as possible
- ensure the distractors are plausible (i.e. common errors made by students)
- use at least 3 distractors (reduces chance of guessing the correct answer)
- avoid distractors that provide clues (e.g. phrases from text books)
- group similar types of MCQs together
- avoid using a pattern for the position of the correct response